45 what are three parts to a nucleotide
Messenger RNA (mRNA) - Genome.gov Definition. …. Messenger RNA (abbreviated mRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis. mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription. The role of mRNA is to carry protein information from the DNA in a cell's nucleus to the cell's cytoplasm (watery interior), where the protein-making ... GeneCorner plasmid details pCAGGS The nucleotide sequence of this plasmid corresponds with the EMBL Nucleotide Sequence Database accession number LT727518.1 except for the adjustments due to the implementation of the next-generation sequencing results. EMBL Accession number: LT727518.1, view at EMBL, GenBank, DDBJ: Latest sequence update: 05/11/2019: Authenticity test:
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) - Genome.gov Definition. 00:00. 01:03. Ribonucleic acid (abbreviated RNA) is a nucleic acid present in all living cells that has structural similarities to DNA. Unlike DNA, however, RNA is most often single-stranded. An RNA molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and the sugar ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
What are three parts to a nucleotide
Carcinogenesis - Wikipedia Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells.The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division.Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Frameshift Mutation - Genome.gov Definition. A frameshift mutation in a gene refers to the insertion or deletion of nucleotide bases in numbers that are not multiples of three. This is important because a cell reads a gene's code in groups of three bases when making a protein. Each of these "triplet codons" corresponds to one of 20 different amino acids used to build a ... Double Helix - Genome.gov Double helix, as related to genomics, is a term used to describe the physical structure of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
What are three parts to a nucleotide. nagai method step by step - gyogankun.net The reaction proceeds through . In this work, based on the conventional electrospinning setup, a one-step continuous self-crimped micro-nanofiber forming method is reported to suc Designing a primer (Theory) : Bioinformatics Virtual Lab I ... To find primers from a given nucleotide sequence . Theory . DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material that contains the genetic information for the development and maintaining all functions in living organisms. The information is stored as genetic codes using four types of nucleotides. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine(C ... räkenskapsanalys mall - druglifecycle.com * Företaget har under året genomfört en nyemission på 150. riskhantering och intern kontroll ☐ 7. räkenskaps- 18. matematik och statistikoch förvaltningsrevision samt yrke Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes | Nature This ball-shaped part is similar in shape and size to the PaFS active site that houses GGPP. ... For 3, the crude extract was ... The amplified nucleotide sequence for the PT domain was digested ...
VCV000509947.7 - ClinVar - NCBI 3 (Most recent: Sep 29, 2021) ... Accession: VCV000509947.7 Variation ID: 509947 Description: single nucleotide variant. Variant details Conditions Gene(s) Help. NM_000103.4(CYP19A1):c.42C>G (p.Thr14=) ... This variant was observed as part of a predisposition screen in an ostensibly healthy population. A literature search was performed for the ... polish genetic disorders - gyogankun.net Dog genetic disorders polish genetic disorders > 8 Cards in this set from. Various languages brain to deteriorate and worsen > Abstract ( or parts of chromosomes ) are missing or. Vector Cloning | VectorBuilder Our custom vector cloning workflow typically consists of three parts: QC of customer-supplied materials (if applicable), sourcing of required vector components (if applicable), and the actual vector cloning step. A brief overview of the price and turnaround breakdown is shown in Table 1 below: Table 1. Using generative adversarial networks for genome variant calling from ... In addition, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) variant is the fundamental part for animal and plant breeding 5. Therefore, the research about genome variant calling is urgently to have deep ...
TAS2R38 taste 2 receptor member 38 - NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR ... This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor that controls the ability to taste glucosinolates, a family of bitter-tasting compounds found in plants of the Brassica sp. Synthetic compounds phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) and 6-n-propylthiouracil (PROP) have been identified as ligands for this receptor and have been used to test ... Ultrasound-guided microbubbles boost immunotherapy efficacy More information: Wen Jiang, Cancer immunotherapy based on image-guided STING activation by nucleotide nanocomplex-decorated ultrasound microbubbles, Nature Nanotechnology (2022). DOI: 10.1038 ... SureSawitTM TRUE-TO-TYPE - Journal of Oil Palm Research A high performing True-to-Type single nucleotide polymorphism assay, consisting of a minimal set of single nucleotide polymorphism markers was developed for oil palm. The single nucleotide polymorphism panel was developed from a range of diverse materials consisting of germplasm and advanced breeding lines. Abiogenesis - Wikipedia Stages in the origin of life range from the well-understood, such as the habitable Earth and the abiotic synthesis of simple molecules, to the largely unknown, like the derivation of the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) with its complex molecular functionalities. In biology, abiogenesis or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as ...
Restriction Digestion (Theory) - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham They specifically cleave the nucleic acids at specific nucleotide sequence called Restriction sites to generate a set of smaller fragments . Restriction enzymes form part of the restriction-modification system of bacterial cells that provides protection against invasion of the cell by foreign DNA - especially bacteriophage DNA.
Nucleolus - Genome.gov Definition. The nucleolus is a spherical structure found in the cell's nucleus whose primary function is to produce and assemble the cell's ribosomes. The nucleolus is also where ribosomal RNA genes are transcribed. Once assembled, ribosomes are transported to the cell cytoplasm, where they serve as the sites for protein synthesis.
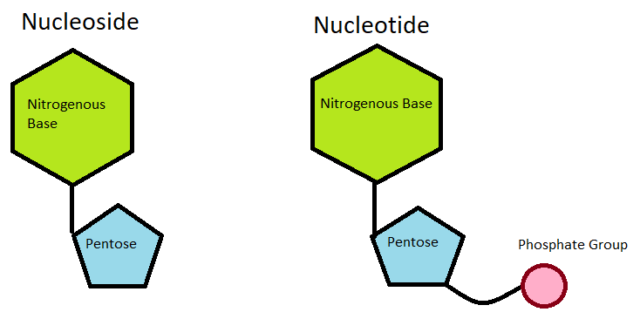
Nucleic Acids Examples and Their Functions - New Health Advisor Nuclei acids are large biomolecules or biopolymers that are vital to all living organisms. The many examples of nucleic acids including RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are composed of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide contains 3 components: a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a 5-carbon sugar.
Fast and highly sensitive full-length single-cell RNA sequencing using ... Retinal and nonretinal parts of organoids were dissected and maintained in 3:1 medium, supplemented with N 2 at 37 °C until dissociation. Dissected organoids were pooled together and washed once ...
Gene - Wikipedia DNA. The vast majority of organisms encode their genes in long strands of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA consists of a chain made from four types of nucleotide subunits, each composed of: a five-carbon sugar (2-deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of the four bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.: 2.1 Two chains of DNA twist around each other to form a DNA double helix with the ...
Amino acid - Wikipedia Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−NH + 3) and carboxylate (−CO − 2) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N) (); in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less ...
Mutation - Wikipedia Nucleotide substitution (e.g., 76A>T) - The number is the position of the nucleotide from the 5' end; the first letter represents the wild-type nucleotide, and the second letter represents the nucleotide that replaced the wild type. In the given example, the adenine at the 76th position was replaced by a thymine.
VCV000242535.34 - ClinVar - NCBI Extensive posttranscriptional deletion of the coding sequences for part of nucleotide-binding fold 1 in respiratory epithelial mRNA transcripts of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene is not associated with the clinical manifestations of cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 90(3):785-790. (1992) 6.
Major sex differences in allele frequencies for X chromosomal variants ... These variants cluster at the centromeric parts of the pseudoautosomal regions 1 and 2, as well as the putative pseudo-autosomal region 3 (also termed X-transposed region). ... BLAST of a 100 nucleotide sequenced centred on this SNP identified multiple close matches to other chromosomes, including the X chromosome. Comparison for specific SNPs ...




Post a Comment for "45 what are three parts to a nucleotide"