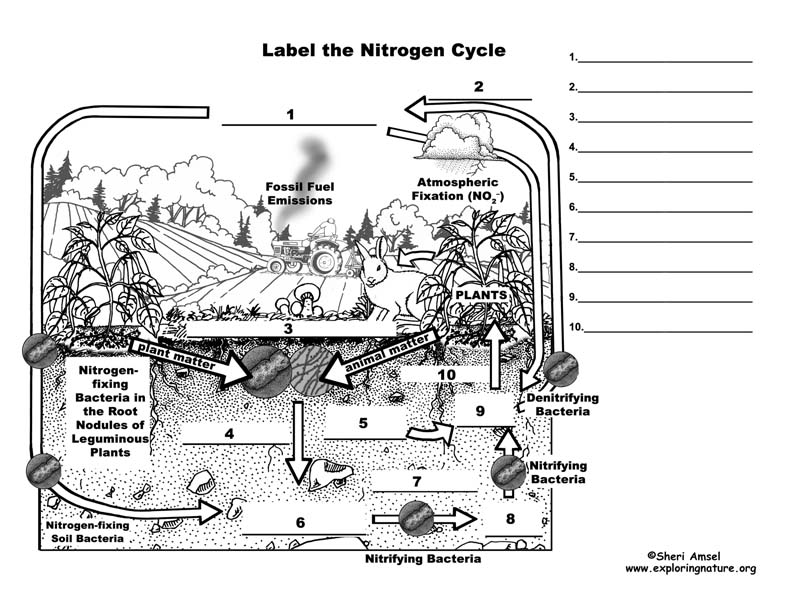
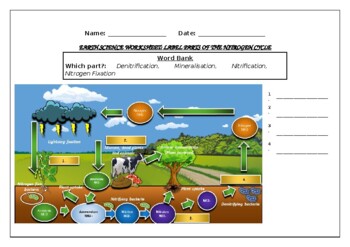
44 nitrogen cycle label
The Nitrogen Cycle - cas.miamioh.edu It is a cycle within the biosphere which involves the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. Nitrogen is found in several locations, or reservoirs. It is most prevalent in sediments and rocks, second in the atmosphere (78%). Approximately 78% of air is Nitrogen. Nitrogen is important to life because it is a key part of amino and nucleic ... Solved 1. Fill in the box below with the name of a | Chegg.com 1. Fill in the box below with the name of a compartment from either the carbon or the nitrogen cycle. Label the left arrow with a type of transfer which brings the element into this pool, and the right arrow with a process which removes the element from this pool. 2.
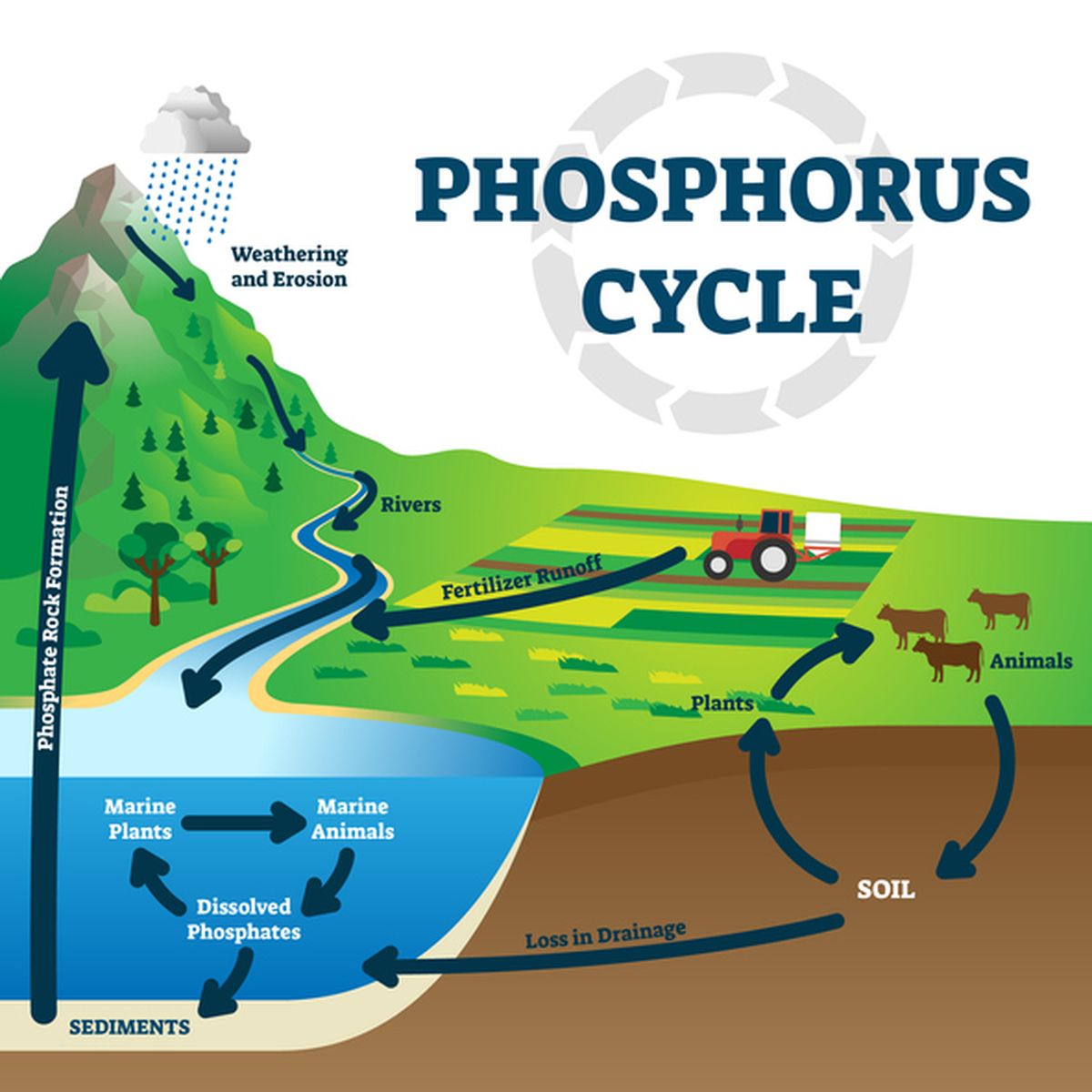
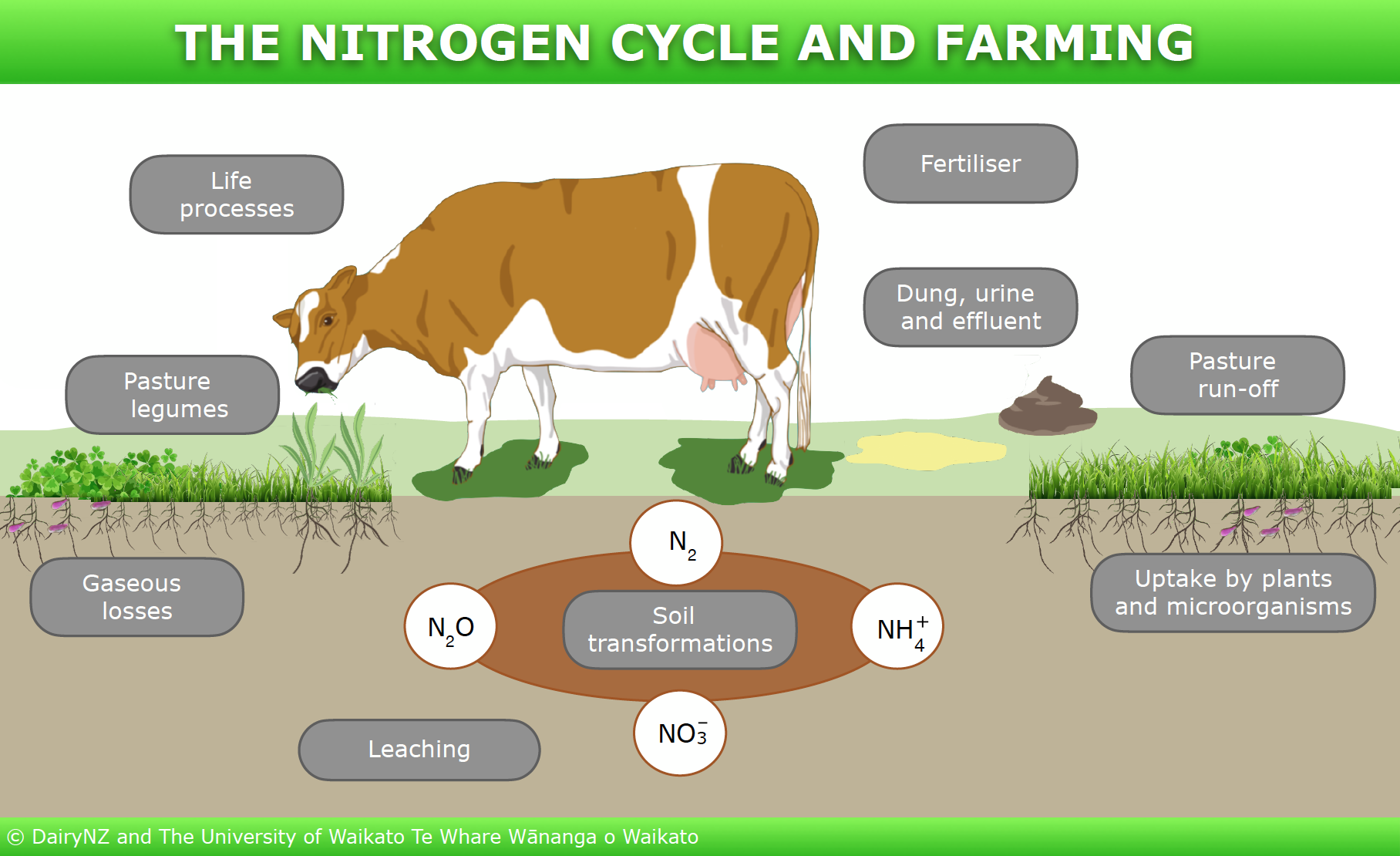
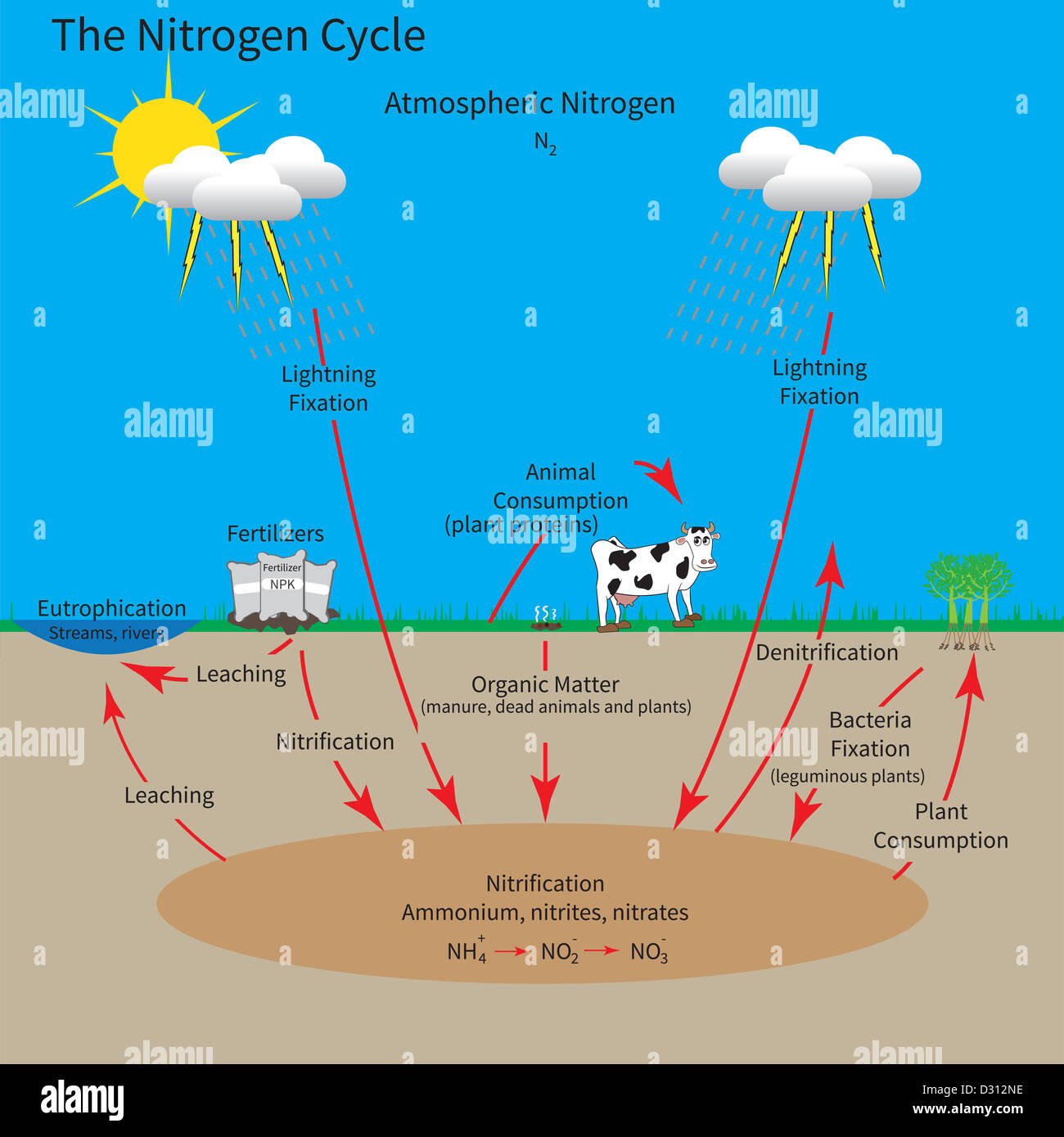
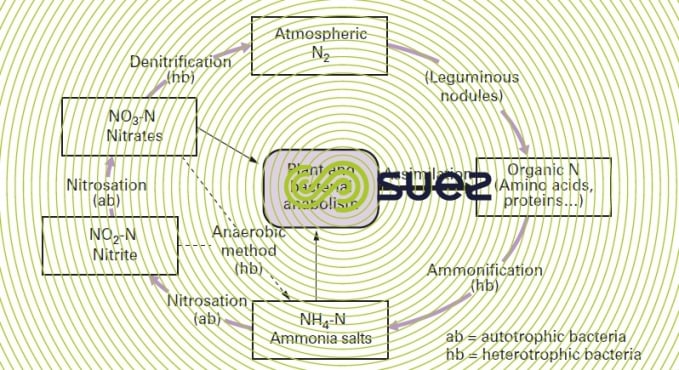
PDF Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles - Weber State University Nitrogen Cycle—Nitrification ! NH 4 + → NO 2-→ NO 3 - " Oxidation of NH 4 + provides electrons, energy " In soil, one species oxidizes NH 4 + to NO 2-! Nitrosomas " 2nd species oxidizes NO 2-to NO 3 - ! Nitrobacter ! Excessive fertilizer use causes nitrate runoff
Nitrogen cycle label
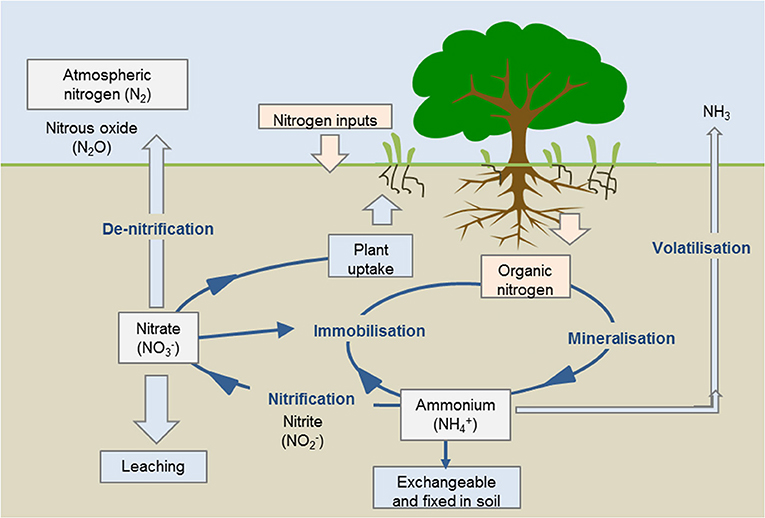
Nitrogen Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics In order for nitrogen to be used for plant growth, it must be available in inorganic formal ammonia (NH 3), ammonium (NH 4), nitrite, (NO 2), or nitrate (NO 3).In the terrestrial nitrogen cycle (Figure 4), soil nitrogen cycling processes dominate, with surface application (fertilizer and manure) providing most of the nitrogen inputs.Microbes break down organic matter to produce much of the ... Nitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and Importance - BYJUS Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction. AP Environmental Science - Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen is a nutrient for amonio acids, proteins, and nucleic acids (such as, DNA and RNA). Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient for plant growth. Animals recieve the nitrogen they need for metabolism, growth, and reproduction by the consumption of living or dead organic matter holding onto molecules composed partially of ...
Nitrogen cycle label. DOC Cycles of Matter Booklet (R) - San Juan Unified School District Page 8 and 9- Nitrogen Cycle _____/10 points *Draw a diagram of the nitrogen cycle- label and color it. *Define the term - Nitrogen Fixing *In your own words, explain what happens in the nitrogen cycle. *Name two factors that could/would disrupt your cycle and explain how/why. Back Cover- Author Biography _____/5 points Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Steps, Importance and Solved Example Nitrogen cycle: 1. Free nitrogen from atmosphere is converted into nitrates by bacterias or by lightning. 2. Nitrates mix with soil, is absorbed by the plants to make proteins. 3. The proteins in plants and animals are converted into amino acids and ammonia. 4. Label the Nitrogen Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Label the Nitrogen Cycle STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match Created by Marlene_Barrientos Terms in this set (8) Nitrogen in air ... Nitrogen fixation: Lightning does some of the nitrogen fixing by breaking nitrogen gas apart and converting it into a usable form. ... Nitrates are also in fertilizers ... Science for Kids: Nitrogen Cycle - Ducksters The nitrogen cycle describes how nitrogen moves between plants, animals, bacteria, the atmosphere (the air), and soil in the ground. Nitrogen is an important element to all life on Earth. Different Nitrogen States For Nitrogen to be used by different life forms on Earth, it must change into different states.
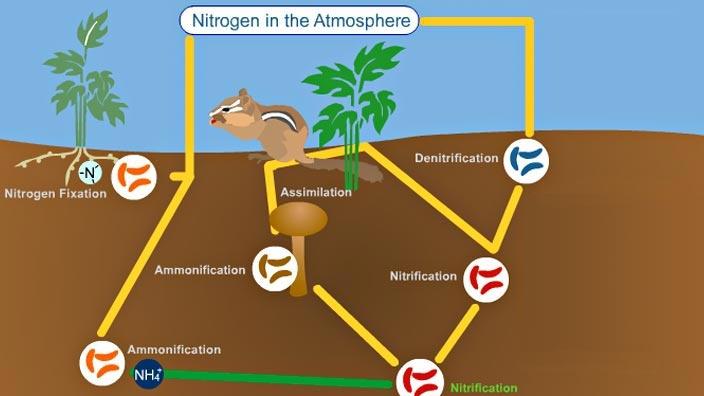
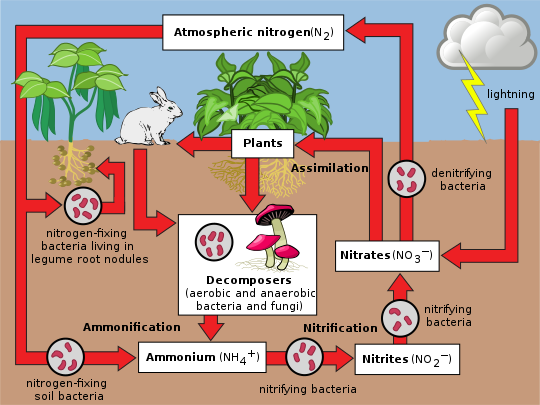
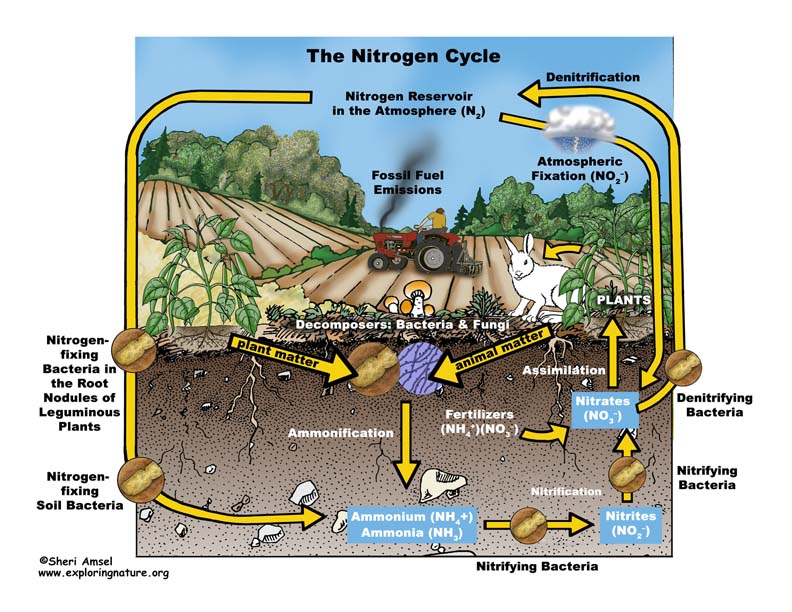
The Nitrogen Cycle and its Processes | Earth Eclipse The major changes in the nitrogen cycle include nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification. These changes to different nitrogen oxides are dependent on various activities of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen Cycle Diagram Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Nitrogen Cycle Doodle Diagrams by Science With Mrs Lau 4.9 (22) $4.00 Zip This set of guided notes with biology doodles on the Nitrogen Cycle can be little anchor charts for your student to keep in their notebook! Using these pages, students can color, doodle, and make connections within the material as they takes notes in class. Diagram of the Nitrogen Cycle | U.S. Geological Survey Detailed Description This diagram of the nitrogen cycle shows were in the cycle antibiotics could impact the ability of denitrifying bacteria to process nitrates and nitrites in groundwater. The diagram is a modified version of figure 9 from USGS SIR 2004-5144, page 16. This study was funded by the USGS's Toxic Substances Hydrology Program. Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) | Ecology - Zoology Notes Once in the biological realm, the first step in the nitrogen cycle is ammonification—a process that involves the hydrolysis of protein and oxidation of amino acids, resulting in the production of ammonia (NH 3 ). This transformation is carried out by all organisms, where during the initial breakdown of amino acids, energy is released (Table 4.4).
NITROGEN CYCLE LESSON PLAN - Kesler Science Students are to draw a picture that demonstrates their knowledge of the nitrogen cycle. Their drawing will have labels such as nitrogen fixing, denitrification, assimilation, ammonification, nitrates, nitrites, plant uptake, dead matter, waste, and nitrogen gas. ORGANIZE IT! Students at this station will match the sets of cards. nitrogen cycle worksheets - TeachersPayTeachers Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet- HS-LS2-4. by. Mrs Bartletts Science and Health Corner. 4.8. (27) $2.99. PDF. This is a worksheet that asks students to answer questions from a diagram of the nitrogen cycle that I drew (I couldn't find one on the internet that I liked). It includes all of the major molecules and processes that take place including ... 5 Stages of Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Nitrogen being 79 per cent of the atmosphere, the atmospheric phase is predominant in the global nitrogen cycle. It is required by organisms in the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other nitrogenous compounds. Atmospheric nitrogen serves as the ultimate source. PDF National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Nitrogen cycle - Wikipedia Simple representation of the nitrogen cycle. Blue represent nitrogen storage, green is for processes moving nitrogen from one place to another, and red is for the bacteria involved Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium Main article: Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium
Nitrogen Cycle - Liveworksheets Nitrogen Cycle Label the nitrogen cycle ID: 1319404 Language: English School subject: Science Grade/level: 7 Age: 9-13 Main content: Science Cycles of matter Other contents: Add to my workbooks (61) Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom
The nitrogen cycle — Science Learning Hub The nitrogen cycle Resource Add to collection Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our planet's atmosphere. Approximately 78% of the atmosphere is made up of nitrogen gas (N 2). Nitrogen is a crucially important component for all life. It is an important part of many cells and processes such as amino acids, proteins and even our DNA.
Nitrogen Cycle - Definition, Steps and Importance - Biology Dictionary Definition. The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins.
Nitrogen cycle | Microbes and the outdoors | Microbiology Society The nitrogen cycle is a series of processes that convert nitrogen gas to organic substances and back to nitrogen in nature. It is a continuous cycle that is maintained by the decomposers and nitrogen bacteria. The nitrogen cycle can be broken down into four types of reaction and micro-organisms play roles in all of these.
Nitrogen Cycle | Components, Process, Role, The Cyclic Path The nitrogen cycle is a closed cycle during which nitrogen present in the atmosphere is converted to chemical compounds that are used by living organisms. Once the organic compounds are used by the living organisms, nitrogen present in them is returned to the atmosphere in gaseous form.
Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Nitrogen cycle, the micro-organisms mediated cycle, is based on four major chemical transformations. (i) Nitrogen fixation where molecular N 2 is fixed as organic nitrogen by Rhizobium bacteria. (ii) Nitrification is the process of oxidising NH 3 to NO -3 by Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. (iii) Nitrate reduction to nitrite ion.
PDF An Introduction to the Nitrogen Cycle - glaquarium.org These movements are called the nitrogen cycle. The nitrogen cycle is one of the biogeochemical cycles and is very important for ecosystems. Nitrogen moves slowly through the cycle and is stored in reservoirs such as the atmosphere, living organisms, soils, and oceans along its way. Most of the nitrogen on Earth is in the atmosphere.
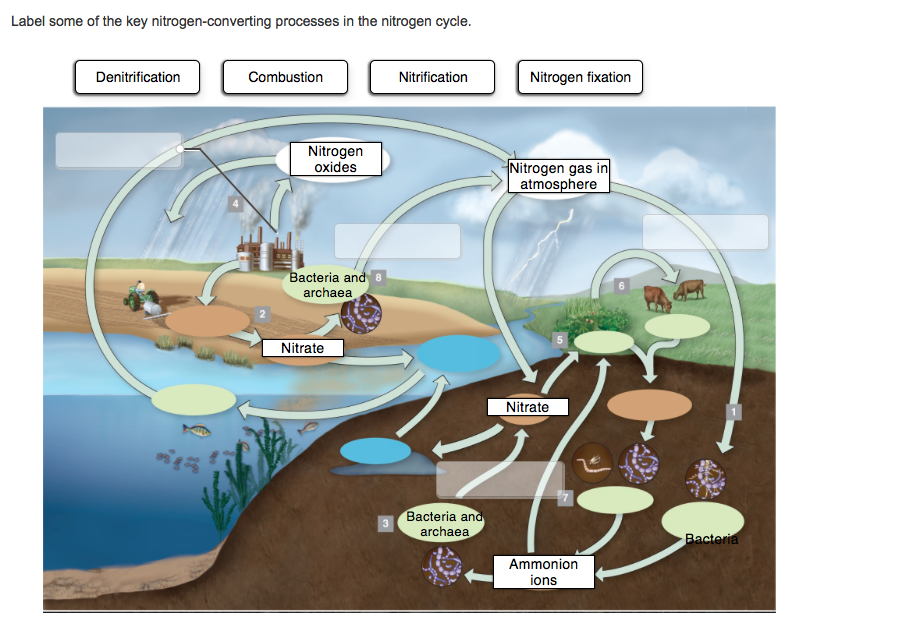
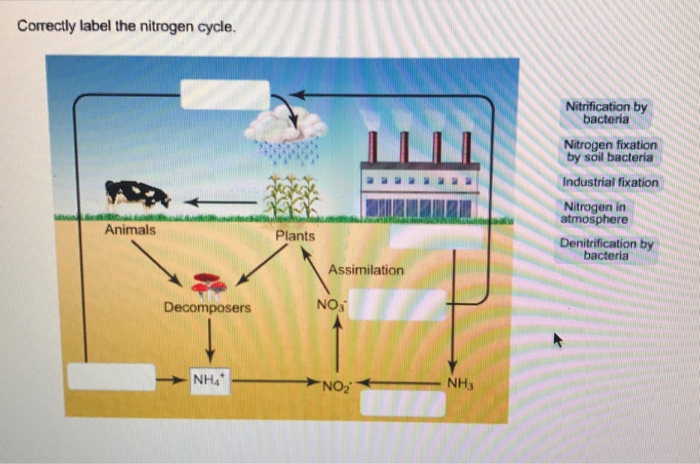
Solved Label the arrows that indicate where processes of the - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (4 ratings) 2. the sun's energy heats the …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label the arrows that indicate where processes of the nitrogen cycle take place. Atmospheric nitrogen (N 2 gas) Answer Bank Producers mineralization Consumers Detritivores, scavengers, decomposers nitrogen fixation, abiotic or biotic ...
What Are the Steps of the Nitrogen Cycle? | HowStuffWorks This is the cycle of a nitrogen atom on Earth, and its journey starts either very quietly or with a humongous bang. Step 1: Nitrogen Fixation. Believe it or not, lightning and bacteria are primarily responsible for turning atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen living things can use. Atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is very stable, so it takes an ...
AP Environmental Science - Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen is a nutrient for amonio acids, proteins, and nucleic acids (such as, DNA and RNA). Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient for plant growth. Animals recieve the nitrogen they need for metabolism, growth, and reproduction by the consumption of living or dead organic matter holding onto molecules composed partially of ...
Nitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and Importance - BYJUS Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.
Nitrogen Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics In order for nitrogen to be used for plant growth, it must be available in inorganic formal ammonia (NH 3), ammonium (NH 4), nitrite, (NO 2), or nitrate (NO 3).In the terrestrial nitrogen cycle (Figure 4), soil nitrogen cycling processes dominate, with surface application (fertilizer and manure) providing most of the nitrogen inputs.Microbes break down organic matter to produce much of the ...




























Post a Comment for "44 nitrogen cycle label"